How to perform a Self-Breast Exam and how frequently should you do it
Breast cancer diagnosis and treatment involve a series of steps to ensure accurate detection and effective management of the disease. Early diagnosis is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Diagnosing Breast Cancer
Breast Self-Exam (SBE)
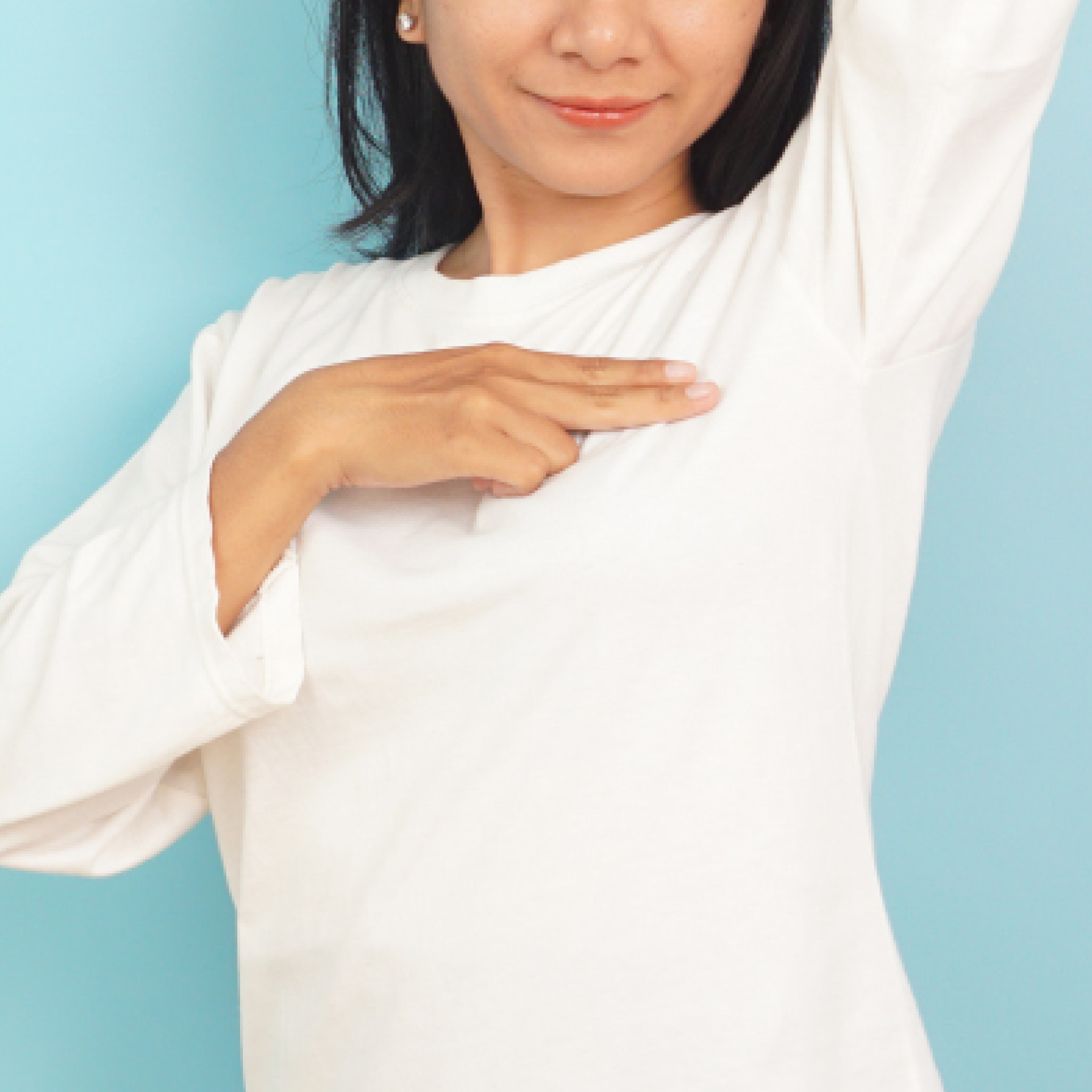

Regular self-breast exams help individuals detect any unusual changes in breast tissue early. While not a substitute for professional screening, it can prompt individuals to seek further evaluation if abnormalities are found.
Clinical Breast Exam (CBE)
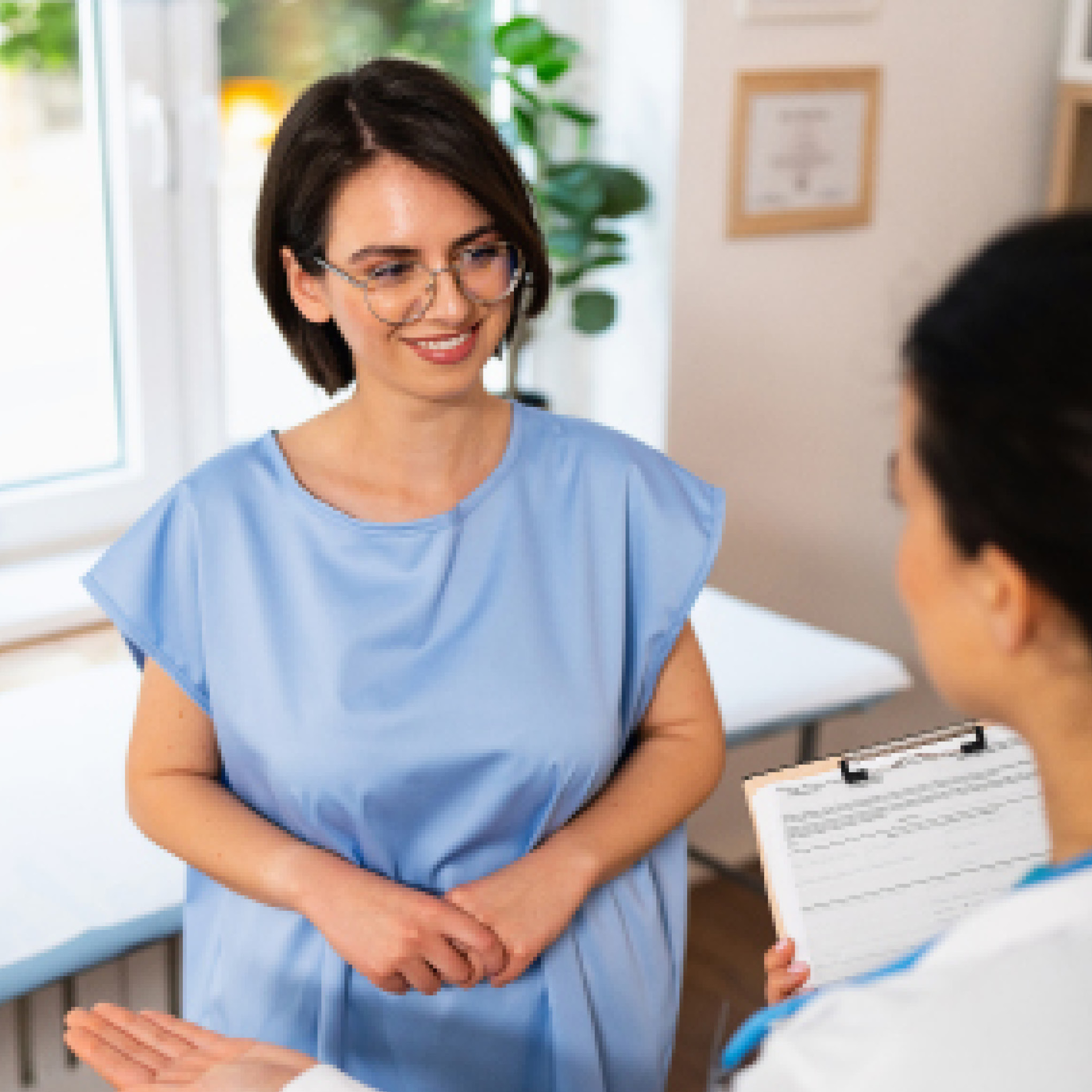

A healthcare professional performs a physical examination of the breasts and underarm areas to check for lumps, swelling, or other unusual changes.
Mammogram
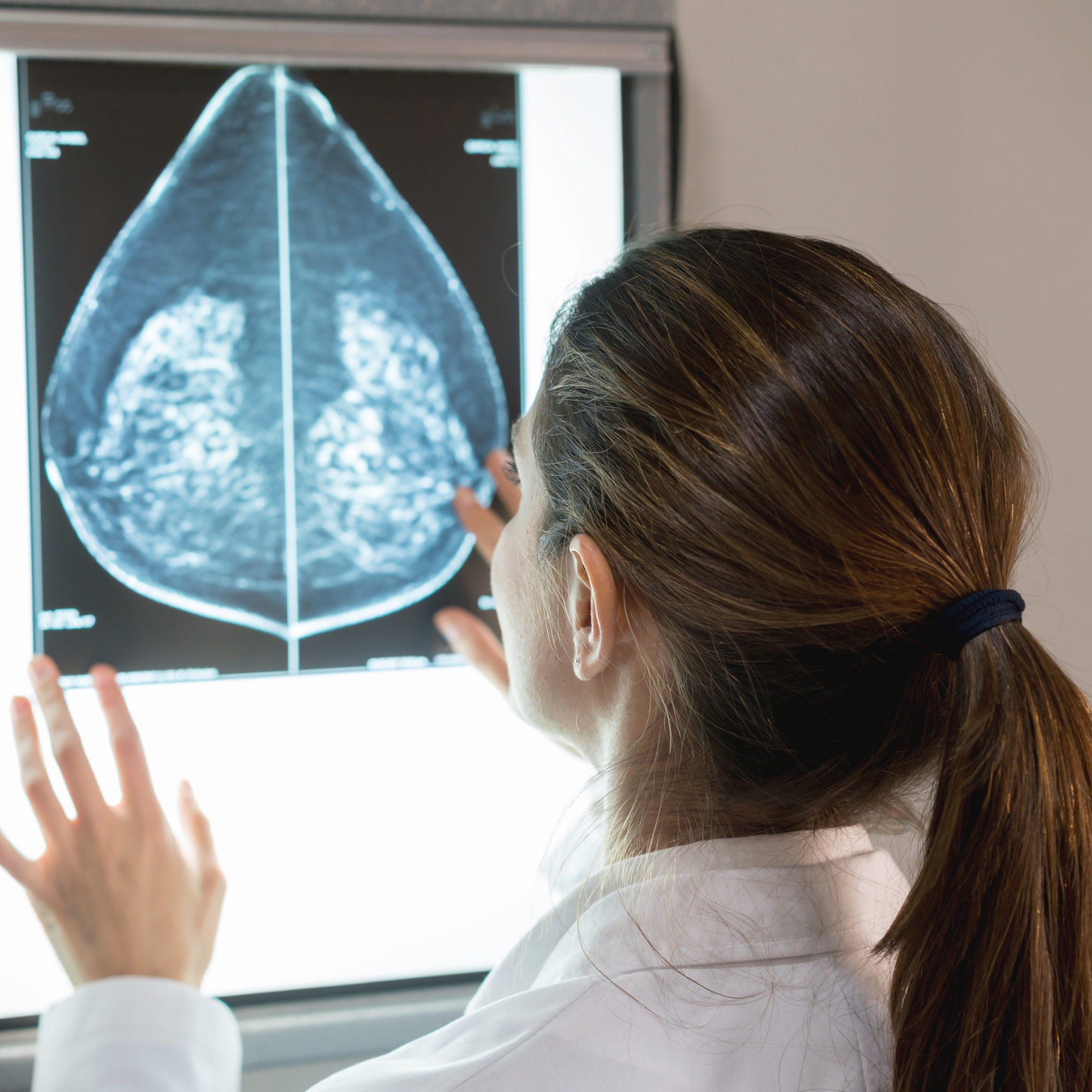
A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast used to detect abnormalities, such as lumps or calcifications, before they are felt. Regular mammograms are recommended for women over 40 or those with higher risk factors.
Ultrasound
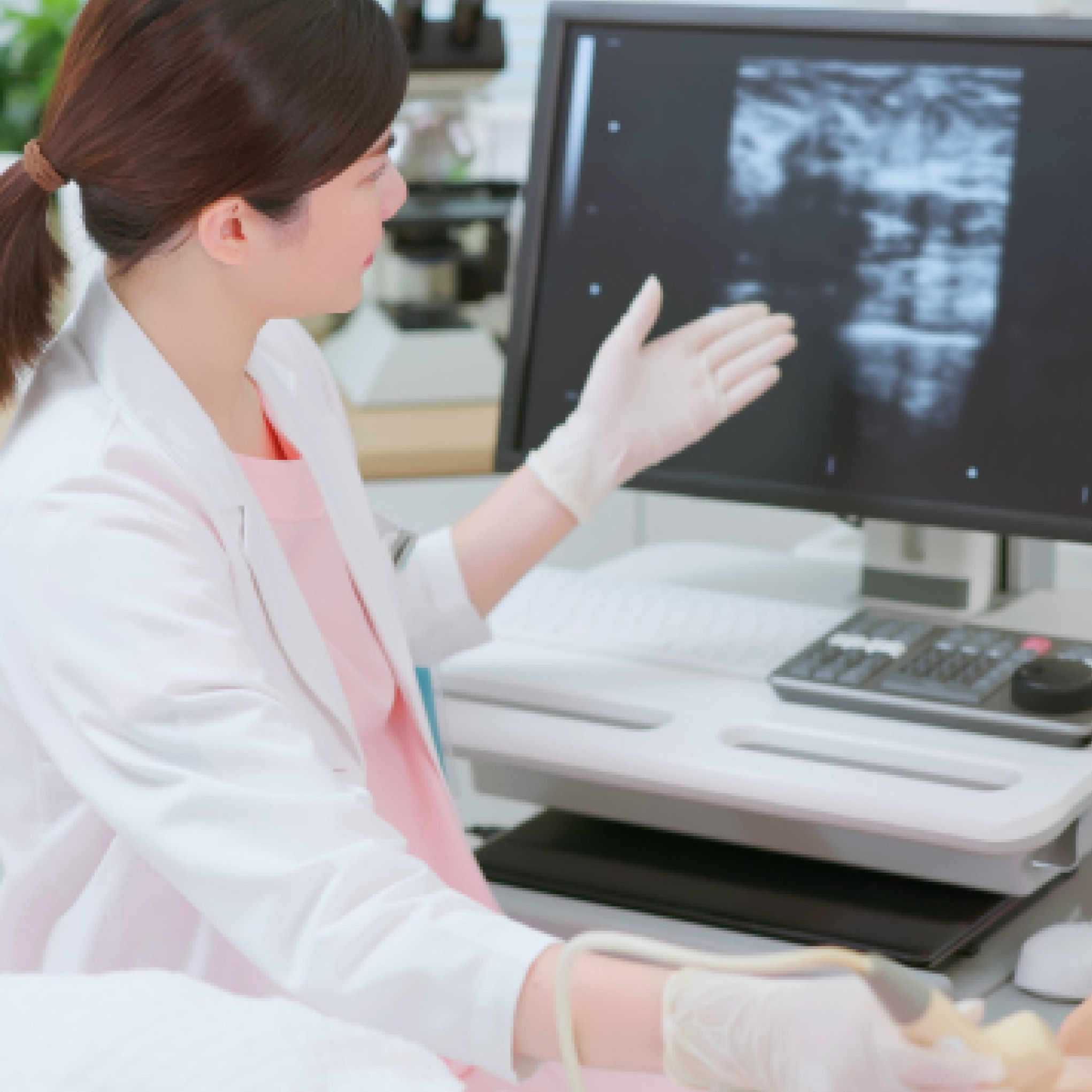
Breast ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of breast tissue. It can help differentiate between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts and is often used alongside mammograms.
Biopsy

If a suspicious area is detected, a biopsy involves removing a small sample of breast tissue for laboratory analysis. The biopsy can be performed using a needle (fine needle aspiration or core needle biopsy) or through a surgical procedure (excisional biopsy) to determine if cancer cells are present.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
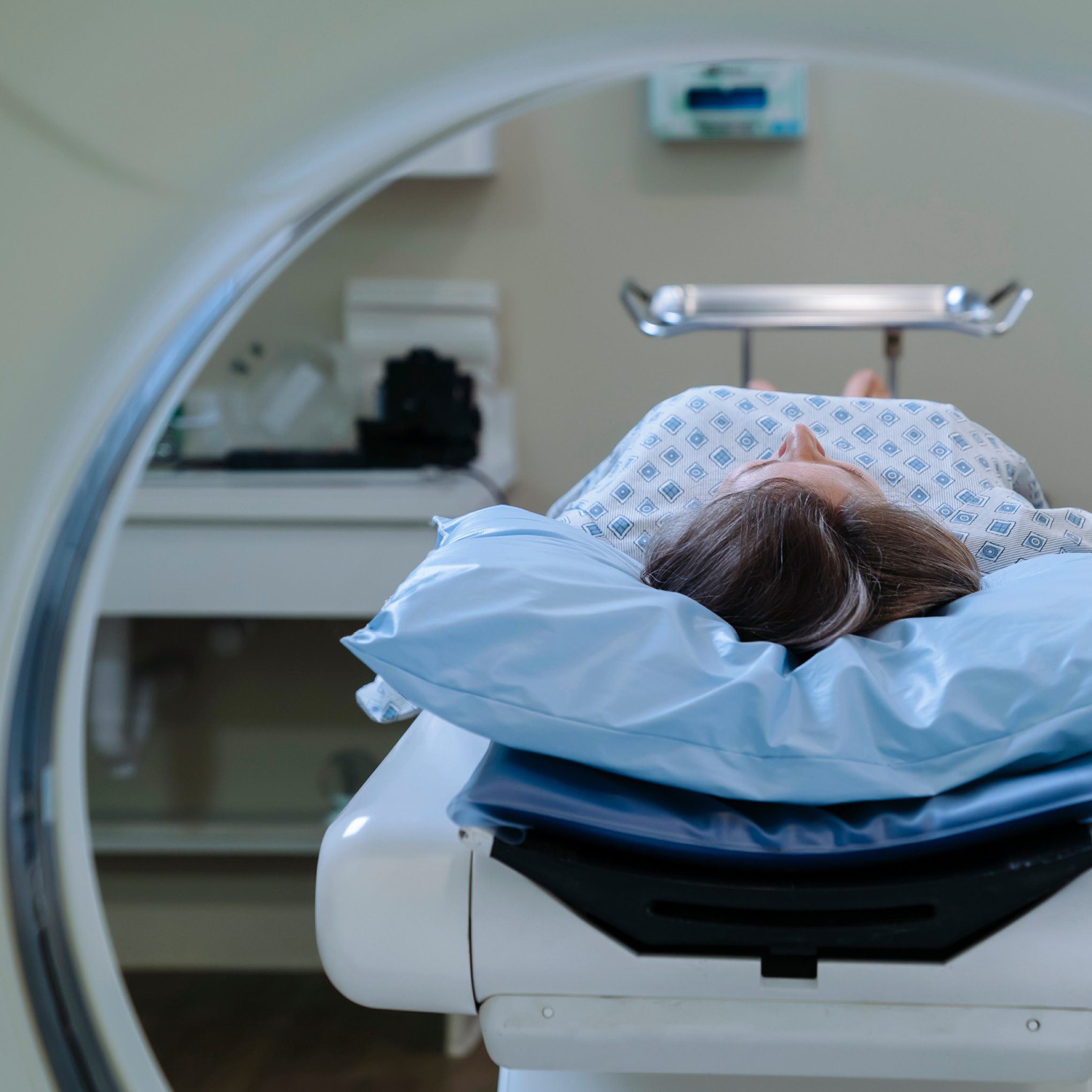
An MRI may be used in certain cases to provide detailed images of the breast tissue, particularly in evaluating the extent of the cancer.
Treating Breast Cancer
Treating Breast Cancer
- Surgery: Surgery is often the first treatment for breast cancer. The options include:
- Lumpectomy: Removal of the cancerous tumor and a small margin of surrounding tissue.
- Mastectomy: Removal of one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) breasts, depending on the cancer’s location and extent.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells in the breast or chest area. It is commonly used after surgery to target any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It can be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant therapy) to shrink tumors or after surgery (adjuvant therapy) to eliminate remaining cancer cells.
- Hormone Therapy: For cancers that are hormone receptor-positive, hormone therapy blocks or lowers the levels of hormones (like estrogen or progesterone) that fuel cancer growth. Common medications include tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies focus on specific characteristics of cancer cells, such as HER2 protein overexpression. These therapies aim to block the growth and spread of cancer cells more precisely.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy works by stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It is a newer approach and is used for specific types of breast cancer.
- Bone-directed Therapy: For cases where the cancer has spread to the bones, treatments may include medications that help protect bones from damage.
Treatment plans are individualized based on the type, stage, and characteristics of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. A multidisciplinary team, including surgeons, oncologists, radiologists, and other specialists, works together to determine the most effective treatment strategy. Regular follow-ups and monitoring are essential to assess treatment effectiveness and manage any potential side effects.
